How To Find The Underground Cable Fault Location?
 Aug 13,2024
Aug 13,2024
 Suke
Suke
It is very difficult for the electricity industry to find underground cable fault locations, especially in some complex power systems. However, a large amount of equipment which has many functions and operates easily appears. In this way, it can not only reduce the high cost of detecting faults but also save time when searching for cable faults. All in all, the updating of industrial equipment has made it convenient to find underground cable fault locations.
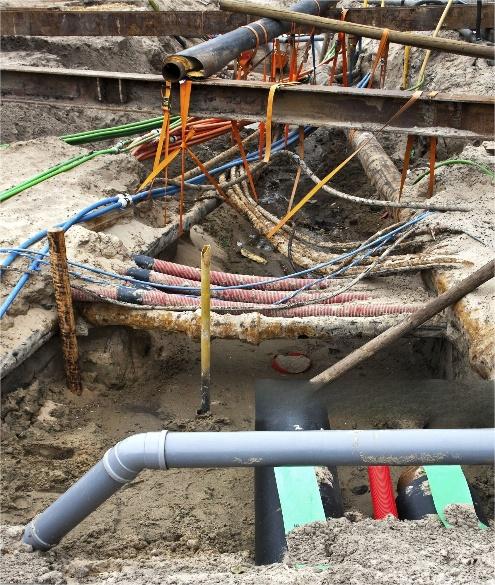

Numerous power companies have adapted impulsion to find faults of underground cable. This method is the most effective method for a simple power system to find faults of high resistance in underground cable. By using pulse or impulsing voltage of outage cables, faults will flash when a valid high-voltage pulse hits the faulty area. Then the operator can hear a kind of hammering sound transmitted along the cable surface. Usually, detecting the fault of underground cable needs a few hammer blows. However, impulsing voltage repeatedly for many times may destroy cables. This method is simple and easy, so some companies have been using impulsion to detect faults of underground cable.
Time-domain reflectometer (TDR) is a kind of low-voltage electric arc reflection equipment that transforms the pulse reflection on the cable structure. This pulse reflection is recorded on the screen of the time-domain reflectometer and compared with characteristic graphs made by sound cables on the same cable route. In addition, operators can also compare graphs of the same characteristics (characteristics performed and recorded before the failure). TDR is one of the most effective equipment for detecting low-resistance faults since the distance to the fault point is determined by the graphical scattering point. The problem is that the analysis of graphs requires trained and experienced operators to operate and analyze. The system of machines that checks high resistance faults of underground cables is always complicated. As a result, the equipment needs a higher energy rating.

Both digital and differential electric arc reflection require special equipment and highly trained operators. Because of the complexity of electric arc reflection, the impulsion remains the most common technique. This technique is relatively simple and does not require special instrumentation or skilled analysts. Instead, the new instrumentation has a variety of functions that can be used for the impulsion to minimize the potential risk to the cable. Using pulses on cables for as short a time as possible and with improved fault detection is a goal shared by many power companies.

 Home
Home Exposure Cable Material Four Major Chaos: Same Appearance And Different Material
Exposure Cable Material Four Major Chaos: Same Appearance And Different Material  You May Also Like
You May Also Like

 Tel
Tel
 Email
Email
 Address
Address