Exposure Cable Material Four Major Chaos: Same Appearance And Different Material
 Aug 19,2024
Aug 19,2024
 Suke
Suke
As we all know, the low-priced bidding system of the cable industry has led to the industry having to reduce the technical indicators and procurement prices of raw materials. In order to get orders, raw material manufacturers killed in the Red Sea market gave up social responsibility and buried many hidden dangers. This article will expose the cable material four chaos that everyone should pay attention to guard against.
1. Low quality antimony trioxide
In flame retardant polyvinyl chloride and flame retardant polyethylene, antimony trioxide is a very efficient flame retardant because it has a good flame retardant co-effect with halogen, which can improve the oxygen index of the material and the material's self-extinguishing performance. However, many material manufacturers use low-quality antimony trioxide containing arsenic trioxide (commonly known as arsenic) to blind many photoelectric cable factories.
Antimony trioxide is a product of stibnite (Sb2O3) calcined oxidation Sb2O3, purified to remove arsenic and iron, and then reduced to metal antimony with carbon, further smelting and purification, and then oxidized to pure Sb2O3. Antimony and arsenic are brothers, so it is necessary to repeatedly purify to remove arsenic.
At present, the arsenic content of high-purity antimony trioxide in China is controlled to ≤300 ppm, but antimony trioxide without repeated purification is also a big market because it is cheap.
At present, antimony trioxide with a purity of more than 99.5% on the market is more than 55,000 yuan/ton, and the so-called antimony trioxide without purification is sold at only 15,000 yuan/ton, and the price difference is nearly four times. If you add 5% of the formula to just this one material, the price will differ by 2000 yuan/ton, but this is not the terrible point of cutting corners.
What is arsenic trioxide? The following quote is from Baidu Encyclopedia: "Arsenic trioxide, commonly known as arsenic, molecular formula As2O3, is the most commercially valuable arsenic compound and the main arsenic chemical starting material." It is also one of the oldest poisons; it is odorless and tasteless, and its appearance is a white frosty powder, so it is called arsenic. It is a highly toxic by-product of the treatment of certain specified minerals, such as gold mining, high-temperature distillation of arsenopyrite, and condensation of its white smoke."
As we all know, arsenic trioxide has long been banned by REACH, but such toxic raw materials are still used by most domestic material manufacturers. Many cable manufacturers do not know how to use them and do not require environmental protection in their procurement standards, in exchange for harm and hidden dangers to front-line personnel and society.

2. Recycled low smoke halogen-free flame retardant materials
The so-called low-smoke halogen-free flame retardant material refers to a flame retardant material that does not contain halogen and has a small amount of smoke. Conventional flame retardants are aluminum hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, phosphorus nitrogen flame retardants, etc., rather than salt flame retardants containing halogens and other heavy metals. However, the quality of materials used in China is uneven, and it is not only unable to meet the physical requirements, but even most of the sheath uses non-flame-retardant calcium carbonate as a filler or directly uses recycled low-smoke halogen-free waste materials.
The optical cable produced by low-smoke halogen-free flame retardant materials has superior flame retardant performance, very little smoke when burning, and no corrosive gas escapes, so it is widely used in nuclear power plants, subway stations, telephone exchanges and computer control centers, high-rise buildings, shopping malls, hotels, radio and television stations, important military facilities, oil platforms, etc., and more concentrated personnel. A place with low air density.
The halogen-free low-smoke and low-halogen low-smoke characteristics of the optical cable mean that when a fire occurs, the spread speed is slow, the smoke concentration is low, the visibility is high, the release of harmful gases is small, and the personnel is easy to evacuate. However, at present, the materials used in China are uneven, and they are not only unable to meet the physical requirements, but even most of the jackets use non-flame-retardant calcium carbonate as filler or directly use recycled low-smoke halogen-free materials.
At present, it is understood that the main types of optical cables involving the use of recycled materials and calcium carbonate filling instead of flame-retardant sheathing are: butterfly optical cables, low-voltage cables, video cables, railway signal cables, etc. It is mainly used in places such as tracks or indoor buildings. The sheath material filled with calcium carbonate is not only non-flame-retardant but also has flammable characteristics and cannot meet the requirements of flame spread speed and combustion smoke. The practice of reducing costs for profit, regardless of the quality of the project,.
The use of recycled plastic as a sheath of optical cables, the service life to be assessed, is the biggest harm because it is easy to aging and cracking. The optical cable core cannot play an effective protective role, so the service life of the optical cable is greatly reduced.
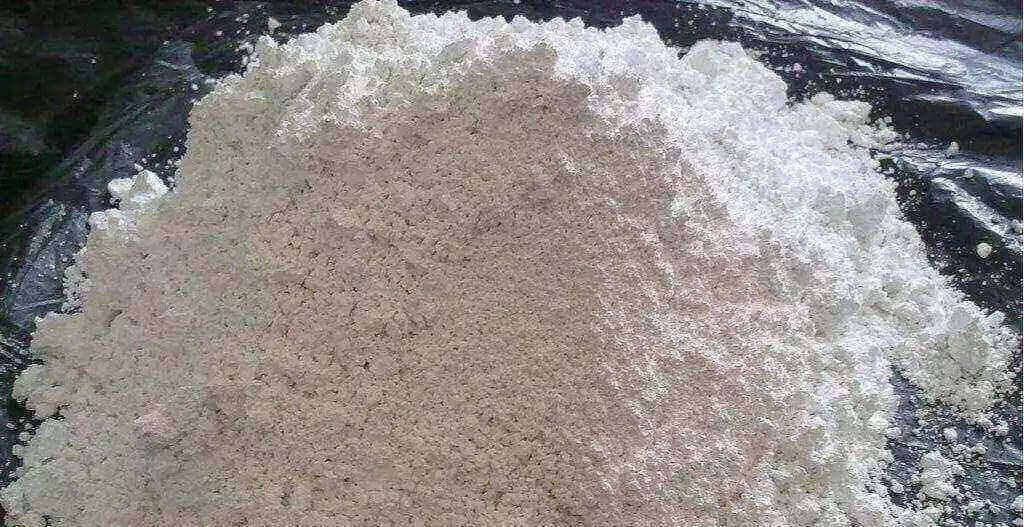

3. Polyethylene recycled materials
Let's talk about polyethylene recycled materials. Recycling itself is the use of waste products in the name of environmental protection. Regardless of the impact of such use in terms of market order, there are huge risks to the product itself. Even if the additive is added again, it cannot make up for the defects generated inside the material, so the service life will be much lower than the new material, and even the situation of aging and cracking will occur in the short term.
When it comes to recycled materials, everyone always asks: What is the difference between new materials and recycled materials? The recycled material is made of plastic products, corner waste recycled and crushed, adding additives, and re-granulating.
Because of the uncertainty of the source of plastic products and corner waste, resulting in a lot of impurities contained in them, the quality is very unstable, and the physical property gap between batches is large. Tensile strength, toughness, and other mechanical and electrical properties are far inferior to the new material. The color of the product will also be dark, with a poor gloss. Most of the recycled ingredients have an odor, some similar to the rich taste of dish soap, and some have a pungent taste.
In addition to the gap in the performance of these materials, the biggest difference is in their use. Because the recycled material contains more impurities, non-decomposing inorganic substances, etc., the surface of the extrusion product will be rough, matte, and even granular, which has a serious impact on the appearance of the product compared to the smooth and delicate surface of the new material.
The oxidation induction period is an index to evaluate the thermal degradation ability of materials during molding, storage, and use. Based on the exothermic reaction when the molecular chain of plastics is broken, the accelerated aging degree of plastics in high-temperature oxygen is tested using differential thermal analysis.
Due to the inconsistency of the source and the characteristics of multiple processing, the molecular chain has been partially broken; even if the additive is added again, it cannot make up for the defects generated within the material, so the service life will be much lower than that of the new material, and even aging and cracking will occur in the short term.
4. Low price PVC cable material
Soft PVC material has good electrical, mechanical, physical, and electrical properties. It has wide resources and a low price, and it is widely used in all kinds of wire, cable, and optical cable. However, in recent years, some cable material companies have used low-quality and low-cost so-called substitute plasticizers to produce low-cost PVC cable materials that seriously do not meet the requirements of the standard.
The most commonly used PVC cable material is the so-called epoxy fatty acid methyl ester, which is actually epoxy "gutter oil," which is a chemical product obtained from various types of gutter oil after oxidation treatment. What is the result of its addition to the cable material, and what are the hazards to the performance of the material and the long-term use of the cable?
Epoxy fatty acid methyl ester has a flash point of 170 ~ 190 °C, and PVC resin has a certain compatibility. There is a great risk of precipitation after the addition of PVC, which manifests as oil in summer and frost in winter. According to different formulations and processing processes, the precipitation time is also different; some have a performance in one or two months, and some may take one or two years or even several years to show.
Cables made of such materials will continue to exhibit the phenomenon of oil and white with the increase in laying time. In addition, with the increase in its addition component, it is easy to cause thermal aging mass loss and unqualified, and a large amount of addition causes serious unqualified.

 Home
Home Why Substation Is Necessary In A Power System?
Why Substation Is Necessary In A Power System?  You May Also Like
You May Also Like

 Tel
Tel
 Email
Email
 Address
Address