What Is Shielded Cable And Damage Prevention Methods?
 Aug 12,2024
Aug 12,2024
 Suke
Suke
Shielded cable is a transmission line that uses a metal mesh braided layer to wrap the signal line. The braided layer is usually made of red copper or tinned copper. Shielding is intended to ensure the transmission performance of the system in an electromagnetic interference environment; the anti-interference should include two aspects: the ability to resist external electromagnetic interference and the ability of the system itself to radiate electromagnetic interference. In theory, wrapping a layer of metal material around the exterior of shielded cables and connectors can effectively filter out unnecessary electromagnetic waves, but how effective is this method?
For the shielding system, a single layer of metal shielding is not sufficient; more importantly, the shielding layer must be properly grounded to ensure that the interference current can be effectively directed into the ground. However, there are several challenges that cannot be overlooked in the construction of the shielding system: due to the stringent grounding requirements, it is easy to encounter poor grounding conditions, such as excessive grounding resistance and uneven grounding potential. This can lead to potential differences between certain points in the transmission system, resulting in current flow on the metal shielding layer, which compromises the continuity and integrity of the shielding layer.
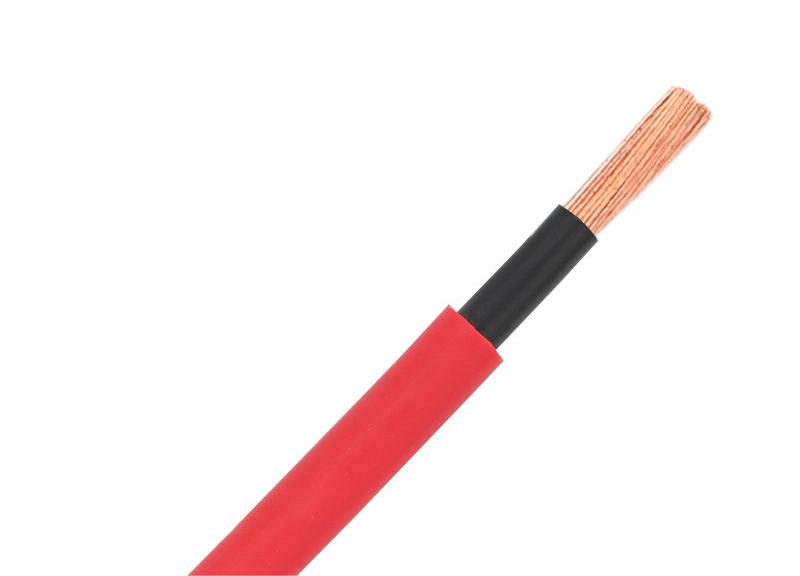

At this time, the shield itself has become the largest source of interference, resulting in its performance being far less than that of the unshielded system. High frequency transmission of the shielded wire necessitates grounding at both ends, thereby increasing the likelihood of a potential difference within the shielded layer. It can be seen that the requirements of the shielding system itself constitute the biggest obstacle to ensuring its performance. A complete shielding system requires shielding everywhere; once any point of shielding cannot meet the requirements, it will inevitably affect the overall transmission performance of the system. However, few network hubs or computers on the market have shielding support, so it is difficult to achieve shielding of the entire transmission link.
In shielded cables used for towing chains, the load on the shielding layer of the outer diameter of the cable must be taken into account. Unreasonable shielding weaving angle will further increase the tension load, resulting in the damage to the shielding layer. This can lead to a weakened shielding effect and even a short circuit when the sharp end of the shielded cable pokes through the wool fabric or foil material and touches the core wire. Here, we recommend a useful tip: if you strip the insulation, you can easily push the shield back into the sheath, but such a shield will not be suitable for the highly flexible cables that are moving in the energy supply system. The shielding weaving angle determined by long-term experiments can effectively counteract the tension, so it is very suitable for towing chains. Due to the stable inner sheath, the shield does not relax and fail. In the twisted wire structure, the shield itself has torsional resistance.
Any defects in the internal structure are difficult to detect from the outside, but problems with the sheathing can be directly observed by the naked eye. The sheath is the first layer of protection for the precise internal structure of the shielded cable. This is why cracked, worn, and inflated sheathing is a very serious quality problem. So what should we do when the sheath is worn or broken?

At this time, we can use armor-type extruded sheaths. Manufacturing processes and materials are also important factors in determining product quality. In some of the so-called cables suitable for drag chains, the sheath is usually tubular, so it cannot provide the necessary support for the twisted wire structure during the long-term bending process, so the twisted wire structure is easy to split. The invention relates to an armor-type extrusion-forming sheath. This sheath ensures that the core of the shielded cable will not loosen when it is in motion. The reason is that the sheath is extruded by a particularly large pressure; it is like a guide groove, which guides the movement of the core wire and also plays a supporting role. Therefore, it is very suitable for towing chains.

 Home
Home How To Find The Underground Cable Fault Location?
How To Find The Underground Cable Fault Location?  You May Also Like
You May Also Like

 Tel
Tel
 Email
Email
 Address
Address