What Are The Common Burial Methods For Submarine Cables?
 May 09,2024
May 09,2024
 Suke
Suke
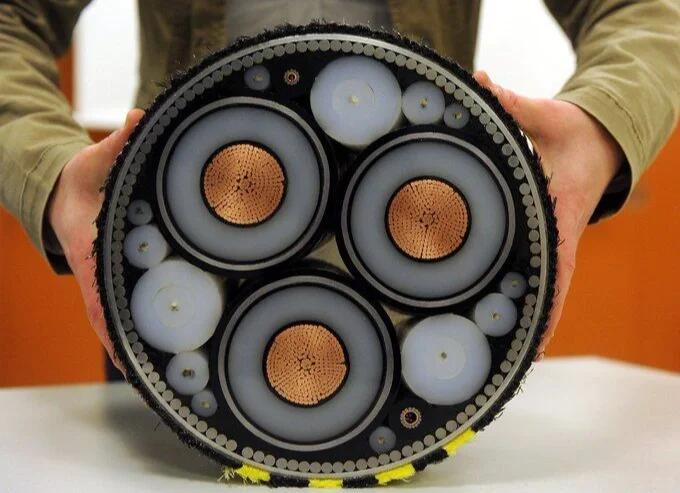

1、The excavation technique:The excavation method is a primary technique for dredging channels, widely employed in intertidal zones and frequently utilized for the construction of submarine cables in narrow sea areas such as river crossings, straits, and main channels. While the excavation method can effectively meet burial depth requirements, it significantly impacts main channel navigation and necessitates longer periods of sealing or semi-sealing, resulting in higher construction costs. Currently, this method is generally not employed in submarine cable construction. The excavation method involves using a dredger to excavate according to the desired burial depth. Once excavated, the cable is directly laid down, and the soil is backfilled by tidal action. To achieve a certain width and depth during excavation, specific slope proportions must be maintained; otherwise, landslides may occur.
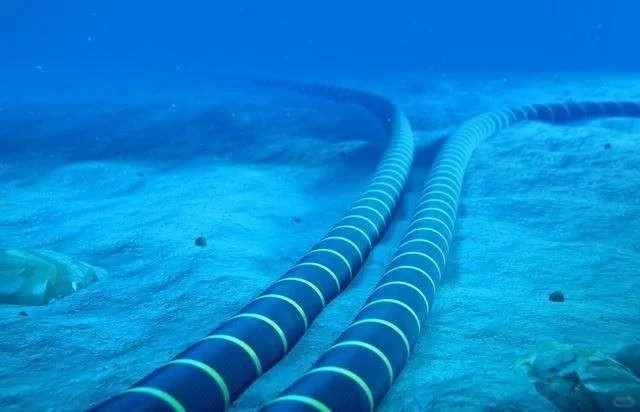

2、Construction method of knife plow buried plow: The knife plow buried plow construction method involves the use of a submarine cable construction ship to lay the cable while dragging the buried plow with its strong tractive force. This causes the knife plow, located at the end of the buried plow, to excavate a trench on the seabed where the submarine cable is subsequently buried. The depth of burial can be adjusted by controlling the hydraulic device equipped on the main body of the buried plow, along with various sensors and television cameras for monitoring its posture, obstacles, and the introduction of submarine cables. Additionally, an onboard signal processing device is utilized to send control signals to both TV cameras and other components of the buried plow body while collecting relevant data. During burial operations, power supply and control equipment from a monitoring room on board supplies power to operate and control the buried plow. This construction method requires a large submarine cable construction vessel with enhanced traction, and the submarine cable can be buried in various types of submarine sediments except for rocks. Under normal circumstances, it is easier to construct in mud texture, while sand texture construction offers relatively higher strength. In the laying of deep water and long-distance submarine cables, the knife plow burial method is commonly employed due to its advantages, such as requiring fewer auxiliary vessels, strong wind resistance, fast construction speed, and high efficiency. However, one disadvantage is that it cannot bury the submarine cable in shallow areas or re-bury it after repair.

3、The punching buried plow construction method involves using a nozzle installed in the cutting part of the buried plow to spray high-pressure water, causing sediment on the seabed to flow and form a trench, where the submarine cable is then buried. This construction method offers several key advantages: simultaneous laying and burying of the submarine cable; ability to bury already laid cables; no strict requirements on tonnage size or tractive force of the construction ship, only requiring sufficient power for water spraying; lower towing tension compared to knife plow burial methods; larger burial depth with a maximum reach of approximately 10m; potential for further improvement in burial depth by combining punching equipment with air lifting and mechanical cutting devices. Additionally, due to its shallow draft, this construction vessel can operate at any water depth ranging from 1.5m to 150m.The submersible construction vessel is not self-propelled and relies on being towed by alternating anchors or other vessels. The buried plow is equipped with sensors, including depth indication, attitude, tension, and pressure, which transmit data to the command center for controlling construction quality. The speed of construction is typically determined by the burial depth. If the control center's computer receives information that meets the required burial depth, it will direct the vessel to move; otherwise, burial will continue until requirements are met. The burial speed in this method depends on seabed soil quality and burial depth, generally ranging from 1m/min to 10m/min with a punching width of 0.2m to 0.4m. When laying submarine cables in shallow sea areas or across harbors and channels where ships frequently anchor, the thrusting plough construction method is usually adopted due to its efficiency. However, this method requires assistance from divers and is limited by water flow speed and pump pressure; therefore, it can only be applied in sea areas with a maximum depth of no more than 50m. Additionally, multiple auxiliary vessels are needed for this type of construction, as the tonnage of the construction vessel is small and susceptible to wind resistance and climate factors.
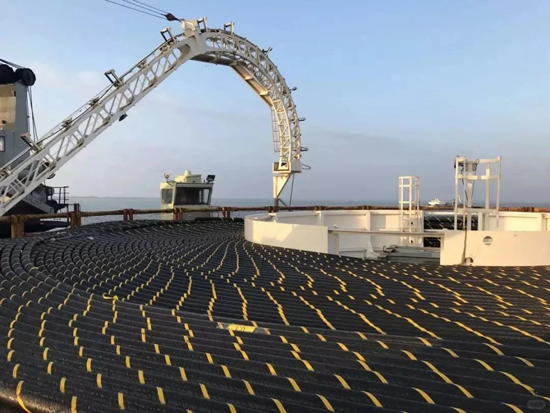

4, ROV flushing construction method: ROV is an underwater remote control vehicle, commonly known as an underwater robot. Each ROV can install two sets of flushing equipment, a cable cutting machine, a clamp to pick up 20t heavy objects, and 25Hz audio signal tracker, and other equipment in each set. ROV can repair and maintain submarine cables in shallow waters up to 2500m deep. In this method, the route of the ROV coastal cable is flushed back and forth, and only one trench with a depth of 0.3m~0.4m and a width of 0.2m can be flushed out each time. The speed of using ROV is slow, the time required is long, and it is only suitable for short-distance back thrust burial construction, which is usually used for maintenance and repair of submarine cables.

 Home
Home What Is The Difference Between Cable And Wire?
What Is The Difference Between Cable And Wire?  You May Also Like
You May Also Like

 Tel
Tel
 Email
Email
 Address
Address