Why Is Market Access For NMD 90 Cable Strict?
 Apr 01,2025
Apr 01,2025
 Suke
Suke
1. Strict electrical safety standards of NMD 90 cable
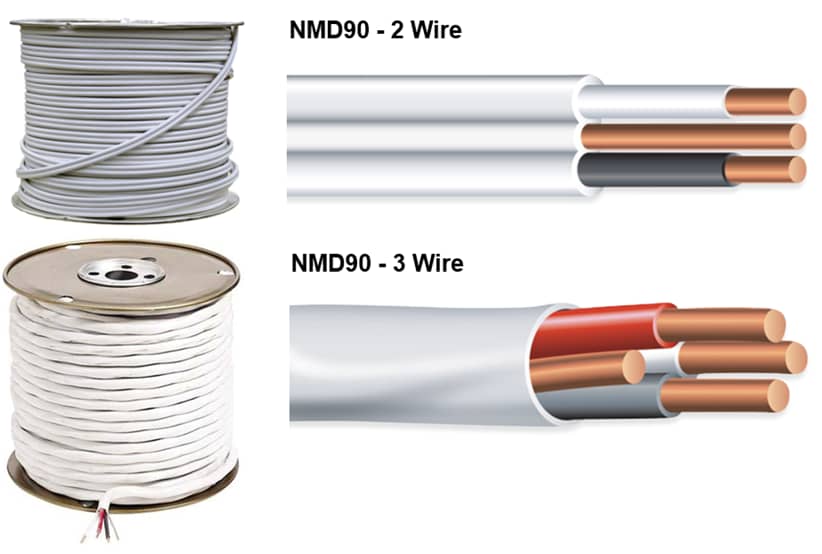
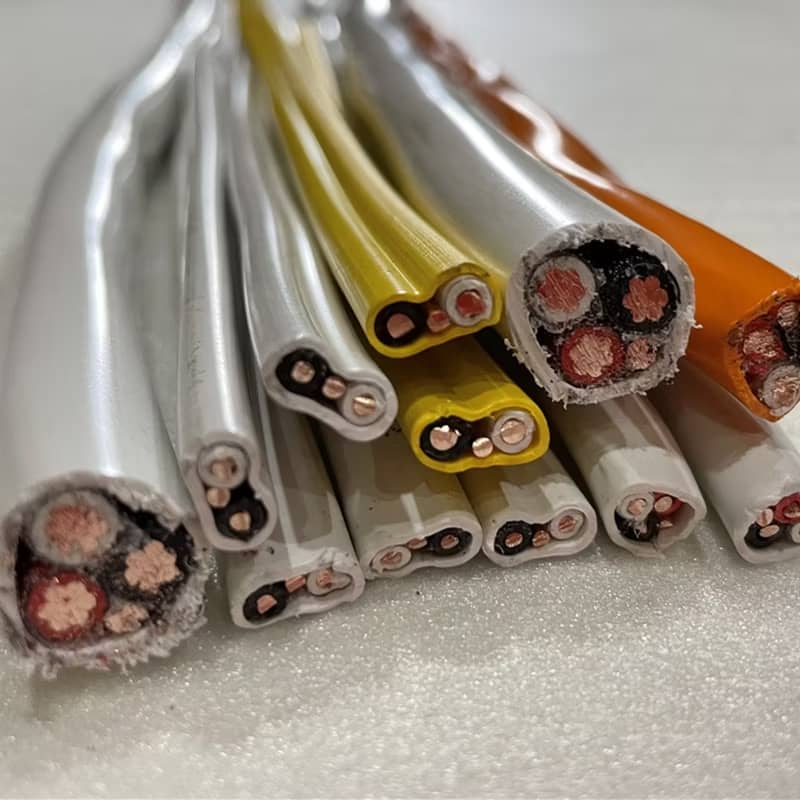
NMD 90 (Non-Metallic Dry, 90℃ rated) cable is usually used in residential and commercial buildings fixed wiring, directly related to the safety of electricity. Once the cable quality is not up to standard (such as insulation failure, insufficient heat resistance), it may cause fire or electric shock.
High certification requirements: In the North American market (such as Canadian CSA certification), NMD 90 cable must comply with CSA C22.2 No. 75 standards, insulation materials, conductor specifications, flame retardant, etc., are strictly tested. Other markets (such as the European Union CE, the United States UL) have similar regulations.
2. Materials and environmental compliance of NMD 90 cable
Flame retardant and low smoke requirements: Construction cables must pass flame retardant (such as UL 1685 vertical combustion test) and low smoke toxicity tests (especially in Europe), and material formulations (such as XLPE insulation) must meet specific environmental regulations (such as EU RoHS, REACH).
High temperature resistance: The stability of long-term work at 90℃ rated temperature needs to be verified, and inferior materials are easy to age, leading to safety risks.
3. Regional barriers to entry of NMD 90 cable
Country/regional differences: For example, Canada requires CSA certification for NMD 90 cable, the US may require UL Listing, and the EU is subject to EN 50575 (CPR Building Products Regulation). Different standards result in high testing and certification costs.
Localization requirements: Some countries require mandatory localization testing or factory review (such as China CCC certification), extending the access cycle.
4. Building regulations and liability traceability of NMD 90 cable
Construction industry supervision: As a hidden engineering material, once there is a problem after installation, the replacement cost is extremely high. As a result, regulatory authorities such as the Canadian Electrical Code (CEC) strictly control access.
Joint liability risk: Developers and contractors tend to choose highly certified products to avoid legal disputes, which indirectly pushes up the market threshold.
5. Competition and market maturity of NMD 90 cable
Leading players: Mature markets (e.g., North America) are already dominated by established brands (e.g., Southwire, Nexans), and new entrants need to invest more resources to prove product comparability.
Customer trust barrier: Buyers often rely on long-term certified suppliers, and the audit of new suppliers is strict.


 Home
Home Quality Testing And Certification Requirements For UL 3132 Wire: How To Ensure Compliance With UL Standards?
Quality Testing And Certification Requirements For UL 3132 Wire: How To Ensure Compliance With UL Standards?  You May Also Like
You May Also Like

 Tel
Tel
 Email
Email
 Address
Address