What Are The Differences Between Fiber Optic Cable And Coaxial Cable?
 Jun 28,2024
Jun 28,2024
 Suke
Suke
Although both fiber optic cables and coaxial cables are communication cables, they differ in the following ways:
Raw material: Fiber optic cable is made of glass or plastic fiber optic core, covered by a plastic PVC jacket. Since the conductor is glass, no current can flow through it and fiber optic cables are not subject to electromagnetic interference. A coaxial cable is a cable with two concentric copper conductors, sharing the same axis with a shielding layer, which is sheathed in PVC or Teflon material. Coaxial cables form a closed electromagnetic field between the inner and outer conductors, so the radiation loss is small.
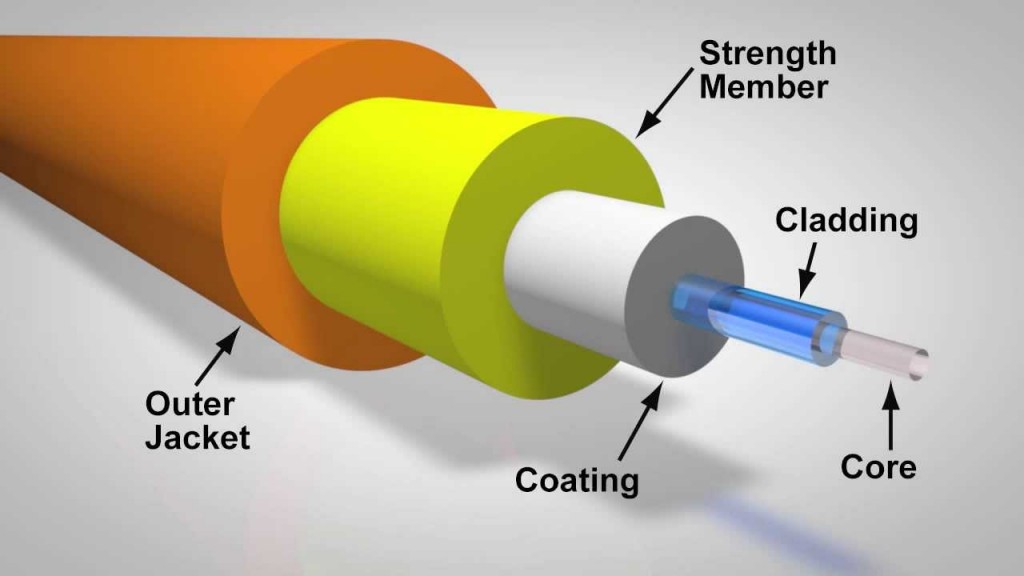
Structure and working principle: Fiber optic cable consists of five parts: core, cladding, coating, strength member, and outer jacket. The implementation of fiber optic cable communications is based on the principle of total reflection of light. Light travels along a fiber optic cable by repeated reflections from the inner walls, where the core and cladding bend the incident light at an angle and have their refractive index. As light signals are sent through the fiber optic cable, they are reflected from the core and cladding in a series of bounces, so light can be conducted from one end to the other. This requires that the refractive index of the core within the fiber optic cable be greater than the refractive index of the cladding for total reflection to occur. Coaxial cables are divided into four layers: center copper wire, dielectric, conducting shield, and outer jacket. It conducts alternating current, the center copper wire, and conducting shield form a current loop, and the electromagnetic field is enclosed between the inner and outer conductors. As the radio emitted from the center wire is isolated by the conducting shield, the conducting shield can be grounded to control the emitted radio.
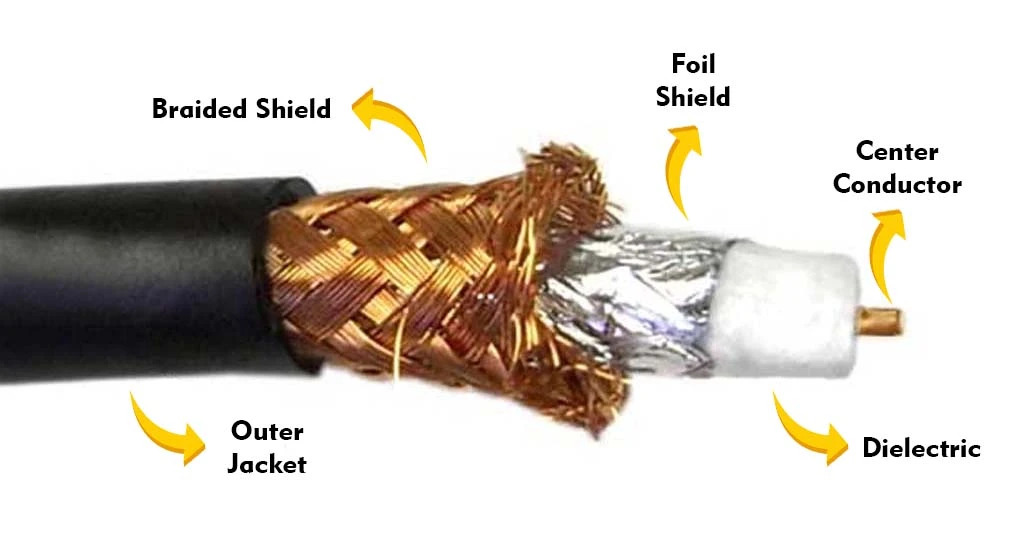
Categorization: There are two types of fiber optic cables, single-mode fiber and multi-mode fiber. Single-mode fibers have a very fine core, about 5-10 microns in diameter, while multi-mode fibers have a core about 10 times the diameter of single-mode fibers. Therefore, single-mode fibers are suitable for long-distance applications between buildings, while multi-mode fibers are suitable for short-distance transmission within buildings. Coaxial cables are divided into two categories: baseband cables and broadband cables. Baseband cables are used only for digital transmission, with a transmission bandwidth of 1 to 20 MHz. Broadband cables are commonly used in CATV, with a transmission bandwidth of up to 1 GHz.
Advantage and disadvantage analysis: Fiber optic cable consists of five parts: core, cladding, coating, strength member, and outer jacket. The implementation of fiber optic cable communications is based on the principle of total reflection of light. Light travels along a fiber optic cable by repeated reflections from the inner walls, where the core and cladding bend the incident light at an angle and have their refractive index. As light signals are sent through the fiber optic cable, they are reflected from the core and cladding in a series of bounces, so light can be conducted from one end to the other. This requires that the refractive index of the core within the fiber optic cable be greater than the refractive index of the cladding for total reflection to occur. Coaxial cables are divided into four layers: center copper wire, dielectric, conducting shield, and outer jacket. It conducts alternating current, the center copper wire, and conducting shield form a current loop, and the electromagnetic field is enclosed between the inner and outer conductors. As the radio emitted from the center wire is isolated by the conducting shield, the conducting shield can be grounded to control the emitted radio.
Uses: Fiber optic cables support maximum connection distances of two kilometers or more, and can therefore be used to form larger-scale networks, such as most Internet, cable television, and telephone systems. Coaxial cables are highly resistant to interference and are widely used for RF or audio/video transmission.

 Home
Home What Is Submarine Cable?
What Is Submarine Cable?  You May Also Like
You May Also Like

 Tel
Tel
 Email
Email
 Address
Address